7.1 KiB
APC P15 Tool
APC P15 Tool is a completely open source application designed to make creating and installing SSL certificates on APC (Schneider Electric) Network Management Cards (2 & 3) simple and easy to do. It is also designed to simplify automation of the certificate management lifecycle.
Background
When APC created the NMC2 (Network Management Card 2), they chose to use
the p15 file format for their SSL keys and certificates, which is a
relatively obscure file format. In addition to this, they designed the
device to require an APC specific header be prepended to the p15 file
or the file would be rejected by the device. Accordingly, they created
a proprietary tool (the NMC Security Wizard CLI Utility) to generate
the required format.
Unfortunately, the proprietary tool has a number of shortcomings:
- It can be difficult to find the right version to use. APC has released a number of versions (in both a CLI and GUI form). Not all of the versions worked correctly (or at all).
- User provided private keys are not supported. Private keys must be generated by the proprietary tool and are only outputted in the p15 format. APC's proprietary tool is closed source and as such there is no way to audit the key generation process.
- Since the generated keys are in the p15 format, they can't be loaded easily into other management tools (such as Cert Warden https://www.certwarden.com/), nor can CSRs be generated easily outside of the proprietary tool. The proprietary tool is generally required to generate the CSR.
- The CSR generation function in the proprietary tool is fairly rigid, making customization (e.g., multiple DNS names) difficult, if not impossible.
- After the user generates a key, generates a CSR, sends that CSR to their CA, and receives a certificate back, they're still not done. The tool must be used again to generate the final p15 file for the NMC.
- To install the final file on the NMC, the user must use an SCP
program such as
pscpto install the file, or the NMC's web UI.
Due to all of this, others have tried to recreate the proprietary
functionality. The only implementations I have found rely on a closed
source library called cryptlib. This library has evolved over time
and more recent versions do not work for the NMC (it appears at some
point cryptlib switched from 3DES to AES and NMC does not support
AES within the p15 file). It was also near impossible to find an old
enough version of cryptlib that would work. Even if one gets this
working, it does not resolve the obscurity of a closed source
implementation and would continue to be subject to potential future
breakage as the cryptlib library continues to evolve.
This project aims to solve all of these problems by accepting the most common key and cert file format (PEM) and by being 100% open source and licensed under the GPL-3.0 license.
Compatibility Notice
Both NMC2 and NMC3 devices should be fully supported. However, I have one NMC2 device in a home lab and have no way to guarantee success in all cases.
Only RSA 1,024, 2,048, and 3,072 bit keys are accepted. 1,024 bit RSA is no longer considered completely secure; avoid keys of this size if possible. Most (all?) public ACME services won't accept keys of this size anyway.
NMC2 does not officially support the 3,072 bit key size, however, it works fine on my NMC2. If you use this size and it doesn't work on your NMC2, try a 2,048 bit key instead. Later versions of the NMC3 firmware support RSA 4,096 and ECDSA keys, but this tool does not. ECDSA was not included in APC's proprietary tool, and as such I have no way to generate files to reverse engineer.
My setup (and therefore the testing setup) is:
- APC Smart-UPS 1500VA RM 2U SUA1500RM2U (Firmware Revision 667.18.D)
- AP9631 NMC2 Hardware Revision 05 running AOS v7.1.2 and Boot Monitor v1.0.9.
If you have problems, please post the log in an issue and I can try to fix it but it may be difficult without your particular hardware to test with.
In particular, if you are experiencing ssh: handshake failed: first try
using the --insecurecipher flag. If this works, you should upgrade your
NMC to a newer firmware which includes secure ciphers. You should NOT automate
your environment using this flag as SSH over these ciphers is broken and
exploitable. If this also does not work, please run ssh -vv myups.example.com
and include the peer server KEXINIT proposal in your issue. For example:
debug2: peer server KEXINIT proposal
debug2: KEX algorithms: diffie-hellman-group-exchange-sha256,diffie-hellman-group-exchange-sha1,ecdh-sha2-nistp256
debug2: host key algorithms: ssh-rsa
debug2: ciphers ctos: aes256-ctr,aes128-ctr,aes256-cbc,aes128-cbc
debug2: ciphers stoc: aes256-ctr,aes128-ctr,aes256-cbc,aes128-cbc
debug2: MACs ctos: hmac-sha2-256,hmac-sha1
debug2: MACs stoc: hmac-sha2-256,hmac-sha1
debug2: compression ctos: none
debug2: compression stoc: none
debug2: languages ctos:
debug2: languages stoc:
Usage
Currently the tool contains two commands: create and install. The tool can be run with the --help flag to see options.
i.e. ./apc-p15-tool --help
Help can also be run on a subcommand to see the options for that subcommand.
e.g. ./apc-p15-tool install --help
Create
Create creates an apc p15 file from given key and cert pem files or content.
e.g. ./apc-p15-tool create --keyfile ./apckey.pem --certfile ./apccert.pem
The command creates and outputs ./apctool.p15 and ./apctool.key.p15 by default. These files are equivelant to the key and final p15 files generated by APC's proprietary tool.
Install
Install generates the necessary p15 file(s) but does NOT save them to disk. It instead installs the files directly on the NMC. Logic automatically deduces if the device is an NMC2 or NMC3 and performs the appropriate installation steps.
e.g. ./apc-p15-tool install --keyfile ./apckey.pem --certfile ./apccert.pem --apchost myapc.example.com:22 --username apc --password someSecret --fingerprint 123abc
Note About Install Automation
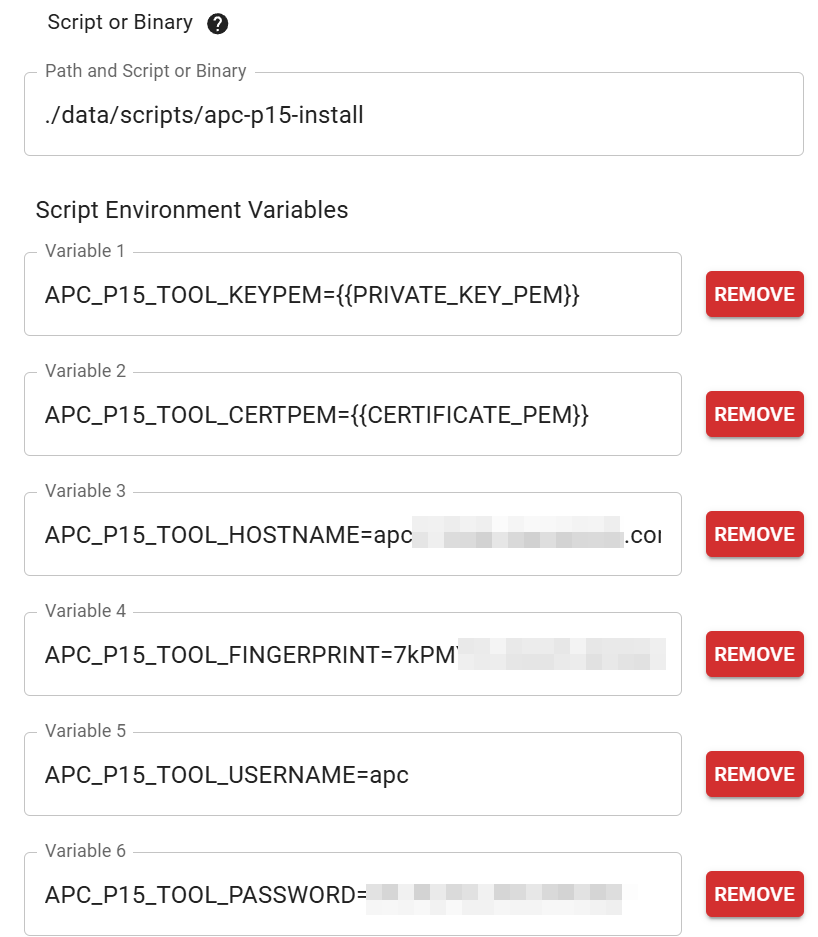
The application supports passing all args instead as environment
variables by prefixing the flag name with APC_P15_TOOL.
e.g. APC_P15_TOOL_KEYPEM
Additionally, there is a second binary built with just the install command so the subcommand is not needed.
There are mutually exclusive flags that allow specifying the pem as either filenames or directly as strings. The strings are useful for passing the pem content from another application without having to save the pem files to disk.
Putting all of this together, you can combine the install binary with a tool like Cert Warden (https://www.certwarden.com/) to call the install binary, with environment variables, to directly upload new certificates as they're issued by Cert Warden, without having to write a separate script.
Thanks
Special thanks to the following people and resources which helped me deduce how all of this works:
https://github.com/dnlmengs/pemtrans